The bicycle carriage is a fairly simple but secretive element. Life is beautiful when the iron horse is in good condition and allows you to cycle kilometer after kilometer. But when there is an incomprehensible crunching, clicking and other unpleasant noises, we have to look for the cause of their appearance in order to prevent a serious breakdown.
The bicycle bottom bracket is screwed or pressed into the bicycle frame sleeve of the same name. It has bearings that drive the connecting rods. This is a very critical element of bicycle construction because it is located close to the ground, so it is often exposed to water, dirt and small debris. Carriages have their own classification, and today we are going to talk more about this small but very important element of bicycle construction.
Components of a bicycle carriage
It traditionally consists of the following components:
- The shaft – which is the moving part that rotates inside the assembly.
- The bearings are located directly inside the carriage base.
- The frame glass – that’s where the entire structure sits.
- The crank mounting clips are the attachments for the connecting rods.
The bearings are attached to the body and the shaft is inserted into the frame cup. The cups are necessary for fixing. The connecting rods, in turn, are tightened on the shaft.
Types of carriages
Classify the discussed element can be according to the peculiarities of the location of the bearings. Depending on this parameter, the following types are distinguished:
- Open. This variety is open to any debris flying from under the wheels, so all components need frequent inspection. And this is a significant disadvantage. As for the positive qualities, it can be noted here the simplicity of maintenance – even an inexperienced master can cope with cleaning and disassembly. The standard type of open carriage is represented by the shaft, which rotates on bearings installed in cups.
- Closed. In this case, the carriage cartridge with bearings in the housing is mounted directly in the frame. Most often this type is found in bicycles of the middle price segment, as it has the greatest protection against dirt ingress. There is a significant disadvantage – the part in case of wear or breakage is not repairable, only replacement. In such a mechanism, bearing distortions are simply excluded, and working with the cartridge – one pleasure.
- Integrated. In this case, the connecting rod with the stars is connected to the shaft in one solid element, which is introduced into the cup of the carriage. This type is also not repairable, but has good performance and reliability.
Rolling bearings for the carriage has its own standards. The following varieties are distinguished:
- Bulk or ball bearings. Already from the name it is clear that the design has balls that roll on the cup. It, in turn, can be removable or pressed into the body of the mechanism. As a rule, this is a budget assembly. The filling mechanism is adjusted by a tapered nut. Beads should be adjusted with caution because if the nut is tightened too much, the wheel will start to spin worse, which will noticeably accelerate the wear on the bushing. If the nut is not tightened hard enough, backlash will form.
- Industrial. Bearings are represented by a non-disassembled assembly, consisting of two rings, between which there are balls. The mechanism is pressed into the seat and is replaced as needed. It is not possible to adjust these bearings. If the mechanism is badly contaminated, only replacement.
How do I know which carriage is on my bike? Here you need to consider that the manufacturers adhere to certain standards, so there should not be any difficulties with the choice of the right part.
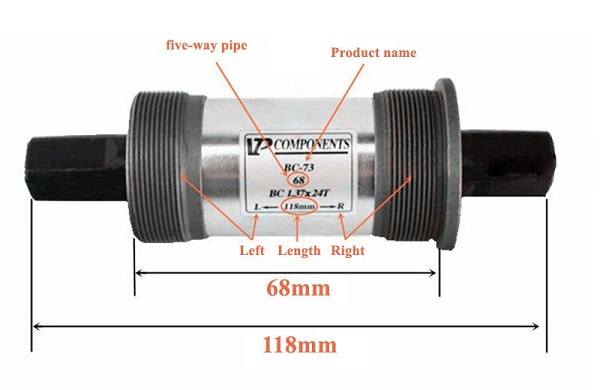
Dimensions
Manufacturers of bicycle frames and parts comply with certain standards. Sometimes a situation can arise where an apparently suitable part does not dock with another element. To determine the width of the carriage, you need to measure the same parameter at the carriage unit of the frame. There are several common options:
- 73 or 68 mm. This value is found on almost all MTB models. A 73 mm carriage can be put on a 68 mm frame if you use three additional rings.
- 83 mm. This size is more common on bikes designed for extreme riding. This parameter is not compatible with the previous size.
- 100 and 120 mm. The less common type, which is applicable to new Fatbikes or extreme bikes.
The size of the design also differs in the length of the shaft. Therefore, to be reliable, you should measure this parameter as well. There are 128 mm, 122.5 mm, 118.5 mm, 113 mm and 110 mm.
Common Standards
Since there are several mounting options for connecting rods to the carriage shaft, there are several common standards:
- Under Wedge. Consists of an axle with grooves through which wedges are inserted into the connecting rods. Each wedge is secured to a groove on one side and a nut on the other. There are also standards here that cannot replace one another. The reason is that the angle of the wedge is different, even though outwardly the size may seem identical.
- Under square. One of the best known types of axle is the SQR. It features a square cross-section of the tapered ends of the shaft on which the connecting rods are mounted. This is a very common option among budget bike models. The carriage has three standards, which are partially interchangeable – there are differences in the length and angles of the cone.
- Octalink. The mount standard is represented by a cartridge carriage with a round shaft. The hollow axle has 8 splines on the ends. This design is able to lighten the weight and increase the strength. This variant is adapted for Shimano systems.
- Isis Drive. The spline standard for most well-known brands. This carriage makes for a reliable mounting and reliability.
- Howitzer. Another spline design, the bearings of which are taken out of the basis of the carriage itself – this allowed to extend the service life of the mechanism. This design is often used on bikes for extreme racing.
- Hollowtech II. This is a product of the famous cycling brand Shimano. The design is represented by a solid carriage system with connecting rods. Its disassembly can only be done from one side of the bike. A compact standard that features increased rigidity, low weight and long service life.
- Giga X Pipe. Analogous to Hollowtech II, but with one nuance – mismatched splines.
As for the configuration, there is a very decent number of options:
- “Spanish”. Not a bad option in terms of the combination of price and quality. Lightweight model with the size of 37 mm. The bearings are pressed into the frame.
- BB90 is analog to the previous model, but with 24 mm shaft.
- MID – another analogue of “Spanish”, but with a difference in the size of the seat (41 mm). Heavier design, but at the same time more reliable.
- BB86 is an analogue of the MID. There are two variations in the width of the cup: 68 mm and 70 mm. The manufacturers produce with outboard and inboard bearings.
- BB92 is an analogue of the previous model, but with different cup sizes (68 mm and 73 mm). Many people complain about the rapid wear of the mechanism.
- The BB30 is a relatively new carriage with the bearings pressed into the assembly. Diameter is 42 mm. Most often equipped with mountain bikes.
- PF30. The variant is represented by two cups without threads with bearings. Characterized by the standard cup size – 46 mm.
It is clear that this is not a complete list of common variants. Manufacturers are constantly working to improve the bicycle design, offering more and more “standards” to improve performance. You can not say that the average user is fundamentally important millimeters and grams of each part. But when it comes to participating in prestigious competitions, it’s that little bit that can make all the difference.
Choosing the right carriage
There’s only one principle here – get the size and type of construction right. To know the width of the carriage, you need to measure the same parameter of the carriage assembly on the frame. Choosing a new part, you should give preference to parts from reputable manufacturers.
And one more point is the bearings. Bulk bearings are not the most reliable option. They are not the most problematic, but they require frequent attention. Cartridge bearings are much better at demonstrating their performance in this regard.
How to determine which carriage on the bike
Masters strongly recommend not to delay with the repair of the carriage mechanism. Problems are eloquently evidenced by a knock at the bottom of the bike, the appearance of backlash and jamming of the carriage unit itself.
To understand which carriage is needed for replacement, you need to pay attention to the following parameters:
- the standard of the connecting rods;
- type of thread;
- the width of the bottom bracket;
- the length of the shaft.
You will have to disassemble the carriage mechanism to make the correct measurements. You can do this yourself, but it is better to contact a bike repair shop, where they will not only tell you what carriage you need, but also perform all the repair and maintenance work on the bike.
Conclusion
Bicycle carriage – albeit a small, but very important element. Its serviceability and impeccable functionality is a guarantee of a comfortable ride and safety. You can choose and replace the carriage yourself. However, given the variety of common standards, it is better to contact an experienced technician.