The bicycle is a practical and, for the most part, versatile means of transportation. It is an economical and convenient mode of transport, which has long been established in the city, the countryside and far beyond the road. The bicycle is also widely used in sports competitions.
On its merits can talk a lot. However, it is worth highlighting the obvious advantage – the primitiveness of design. It is simple and intuitive, which is why the bike is popular among so many people. But his device is not limited to the handlebars, wheels, frame and pedals.
What parts a bicycle consists of
“Anatomy” of a bicycle has much in common with the device of the car – all the working nodes and mechanisms are attached to the supporting structure. Clearly about the structure of two-wheeled transport is evidenced by the diagram “Structure of the bicycle”. From the figure it is clear that all the mechanisms and basic units are held on the bicycle frame.
And now let’s talk in more detail about each part.
Frame
This is a diamond-shaped frame, assembled from several components:
- The front and seat tubes;
- the upper and lower feathers.
The front tubes are “stitched” together into the handlebar sleeve, the bottom and seat tubes together with the feathers into the carriage sleeve, and the feathers between each other into the rear wheel dropouts. The current assortment of bicycles necessitates the classification of frames:
- city models – heavyweight, sturdy and rigid frames;
- mountain models – sturdy, robust and mobile;
- road bikes – their frames are lightweight;
- sports bikes – their frames should be able to withstand enormous loads and be resistant to mechanical damage;
- Trick models – used for BMX bikes.
As for the manufacturing material, there are currently a total of two options: aluminum (budget and the most common) and carbon (the most expensive and wear-resistant).
Saddle
Here you should immediately pay attention to the fact that it is correct to say exactly “saddle” and not “seat”. The fact is that the second option implies deep seating of a person, when the weight of the body is completely distributed over the surface. The saddle of the bicycle has only a partial load. During the movement of the body weight should be evenly distributed between the handlebars, pedals and saddle.
When choosing should be guided by the height of the seatpost. As for soreness in the groin area, it can occur after a long absence of cycling experience. Preference should be given to anatomically shaped saddles from reputable manufacturers.
Handlebar
This part consists of two elements: a horizontal curved tube and a vertical stem. The handlebar can be:
- straight;
- curved up or down;
- “ram’s horns”.
The handlebar stem (can be rigid or adjustable) connects the tube to the handlebar stem. It is a fairly important element of bicycle construction that should be taken seriously. Improperly chosen stem significantly increases the load on the cyclist, as well as affecting some technical points.
The handlebar is an integral element of the bicycle system, which is responsible for the rotation of the bicycle fork in the head frame. It comes in two types:
- threaded;
- unthreaded.
The first option is considered an outdated and cheap design, which will require an adjustable wrench for mounting and dismounting. The threadless headset is found in most modern models – the fork can be easily inserted and fixed in the tube of the steering frame.
Grips
These are attachments for the handlebar grips. This element significantly increases the level of comfort while riding, providing a firm grip. Grips can be plastic or rubber. They are also made of gel, foam, leather, silicone or polyurethane. Preference should be given to durable products that allow you to confidently hold the handlebars even when wet.
handlebar stem
It determines the distance of the handlebar from the frame – the further its remoteness, the more horizontal position the cyclist takes. The discussed part is attached to the adjustment tube.
Shifters
This is one of the elements responsible for shifting gears. Shifters, or shifters, are attached to the handlebars of the bicycle. Their condition determines the clarity of shifting from one gear to another.
Front derailleur
Low-maintenance, hard-wearing shifter that uses a cable to tell the shifter to change gear. It transfers the chain between the sprockets of the front cassette.
Rear derailleur
The mechanism is responsible for the perfect speed change. It shifts the gears of the rear cassette. This is quite a delicate detail, which is open to all the “charms” of bad weather: moisture, dirt, dust, etc. So a lot of attention should be paid to its condition.
Brakes
The brake system of a bicycle – the most important node, on the state of which depends on the safety of the cyclist and other road users. The most common are:
- rim – “ticks”, V-brake;
- discs;
- Drum and hub.
The last type today is extremely rare. Rim clamps are clamping devices with pads that exert pressure on the rims, thereby slowing the movement of the bicycle. Disc brakes consist of a hub-mounted disc, an actuator and a caliper to which the brake pads are attached – this type is the most effective and common. Disc brakes are independent of rim geometry and provide a larger braking surface and shorter pad travel.
Wheels
This is what you can’t imagine a bicycle without. They are lightweight but sturdy structures that include:
- the rim;
- the tube and the tire;
- the hub;
- spokes;
- nipple.
Let’s look at each element of the wheel in more detail.
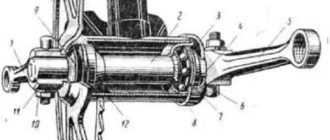
Bicycle hub.
It consists of an axle, bearings, and washers. The hub forms and holds the torque. The internal structure of the discussed rear element is much more complex than the front one, since this part is responsible for spinning the wheel.
Rims .
This is a metal ring that is attached to the hub through the spokes. The features of the rim geometry, coupled with the degree of tension of the spokes determine the resistance of the wheel to mechanical damage and force loads.
Rims are usually made of aluminium alloy, spokes in light metal with chrome plating.
Tires
This is a harmonious tandem of camera and tire. The former is represented by a hollow product of rubber, which is inflated with air to a certain pressure level. Communication with the “outside world” is provided by a nipple through which air is pumped.
The tire or outer part of the tire is characterized by the presence of sides, sidewalls and the contact part (tread), which contacts the surface of the ground. Types of tires:
- Slicks and semi-slicks (they are equipped with highway tires, they are suitable for riding on flat surfaces);
- road (medium tread pattern);
- with an aggressive tread pattern, which allows you to more easily overcome rough terrain;
- Hybrid (from the name it is clear that the tires have characteristics of several types of tires – they can be used both for driving on flat roads and for overcoming off-road; they are much inferior to the aggressive tread pattern).
There are specific tires with grousers at the edges. They are quite comfortable to drive on asphalt, but when driving on loose surfaces – they have no equal.
Pedals
Pedals transmit power from feet to cranks, carriage and front sprockets. There are several types of pedals:
- Classic. A universal type designed for regular cyclists.
- Contact pedals. They are equipped with special inserts that involve the use of special shoes. Due to this feature, a better grip is ensured.
- Extreme. They are used to complete sports bikes. They are thicker, wider and have a fixation insert.
- Mini Pedals.
- Products equipped with straps.
Today, manufacturers offer quite a few options for bicycle pedals, so everyone will be able to individually select the product that meets all the requirements.
Transmission
This is the key mechanism of the bicycle, without which it simply will not ride. The constituent parts:
- drive sprockets;
- gear shifters and rods;
- pedals;
- rear gears;
- carriage;
- chain.
The carriage provides free rotation. It is located in the lower sleeve of the frame and is the connecting element for a pair of connecting rods and front stars.
The “health” of the bicycle’s drivetrain should be given extra attention. Regular inspection, cleaning and lubrication of the elements should become the routine of the cyclist.
Conclusion
The circuit of the bicycle is actually a fairly simple design with a small number of parts and elements. But it is the coordinated work of all components that ensures a comfortable and safe riding. Knowing how the bicycle is set up, you can easily navigate in the range of parts and components.










This post is really informative and the diagram provided makes it easy to understand how a bicycle is built. It’s nice to know what all the different parts of a bike are called!